Thermoradiative System: The Ultimate Guide to Night-Time Energy Generation
Introduction to Thermoradiative System
As the global demand for electricity continues to rise, traditional energy sources are struggling to keep up with consumption, resulting in frequent power shortages and rising energy costs worldwide. In this context, Thermoradiative System (TRD) emerges as an innovative solution, capable of converting low-grade heat into electricity and providing continuous energy, day and night.
This article will explore the fundamentals of Thermoradiative Systems, how they operate, their unique advantages, and the latest research developments, including NASA’s pioneering studies. By the end, you will understand why TRD is considered a game-changing technology for sustainable energy generation globally.
But before we dive deeper into how it works and why it’s gaining global attention, let’s first understand what exactly a Thermoradiative System is — so you can clear any confusion about this next-generation energy breakthrough.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
What is Thermoradiative System?
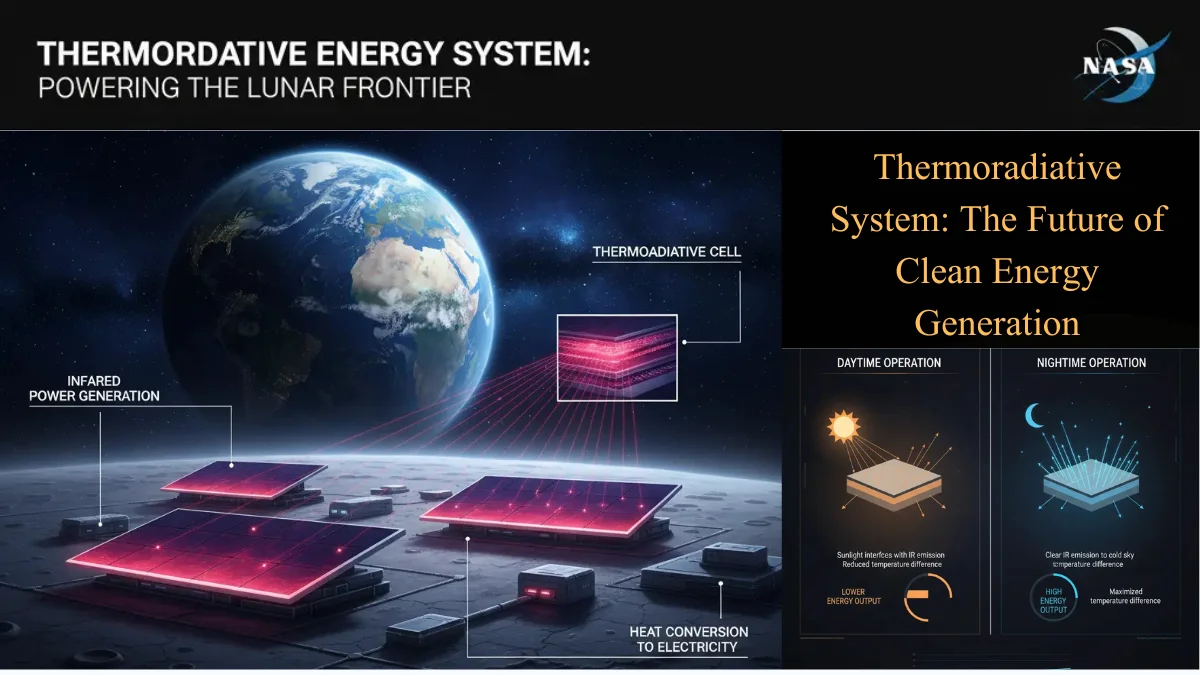
The Thermoradiative System (TRD) is a revolutionary energy technology that converts heat energy directly into electrical energy using high-efficiency semiconductor materials. Its most remarkable feature is that it doesn’t rely solely on sunlight — it can generate electricity even at night, when the temperature difference and natural heat radiation are at their peak.
Traditional solar panels only work when they receive direct sunlight, but the Thermoradiative System is completely different. It operates through thermal radiation and infrared energy. When the Earth releases its stored heat (especially during nighttime), TRD captures that radiation and converts it into usable electricity, ensuring a continuous power supply around the clock.
Now that you have a clear idea of what a Thermoradiative System is and how it differs from traditional solar technologies, the next question naturally arises —
How does this system actually work?
Let’s explore in the next section how the Thermoradiative System operates on its working principles and how it has the ability to generate power even in complete darkness. ⚡
Key Features of Thermoradiative System:
• Utilizes infrared radiation and thermal radiative cooling principles
• Converts low-energy photons using advanced semiconductor technology
• Operates both day and night, unlike conventional solar systems
• Highly sustainable and environment-friendly energy solution
Major Benefits:
• Enables continuous night-time electricity generation
• Offers a reduced carbon footprint and lower environmental impact
• Can complement existing solar and wind systems for 24/7 power production
• Ideal for urban and remote areas where solar efficiency is limited
• Can utilize industrial waste heat for additional power generation
How Thermoradiative System Works
The Thermoradiative System (TRD) works on the principle of converting heat energy and infrared radiation into electrical energy through specially designed semiconductor materials. This technology utilizes quantum efficiency and low-energy photon absorption to generate electricity — even at ambient temperatures, without requiring direct sunlight.
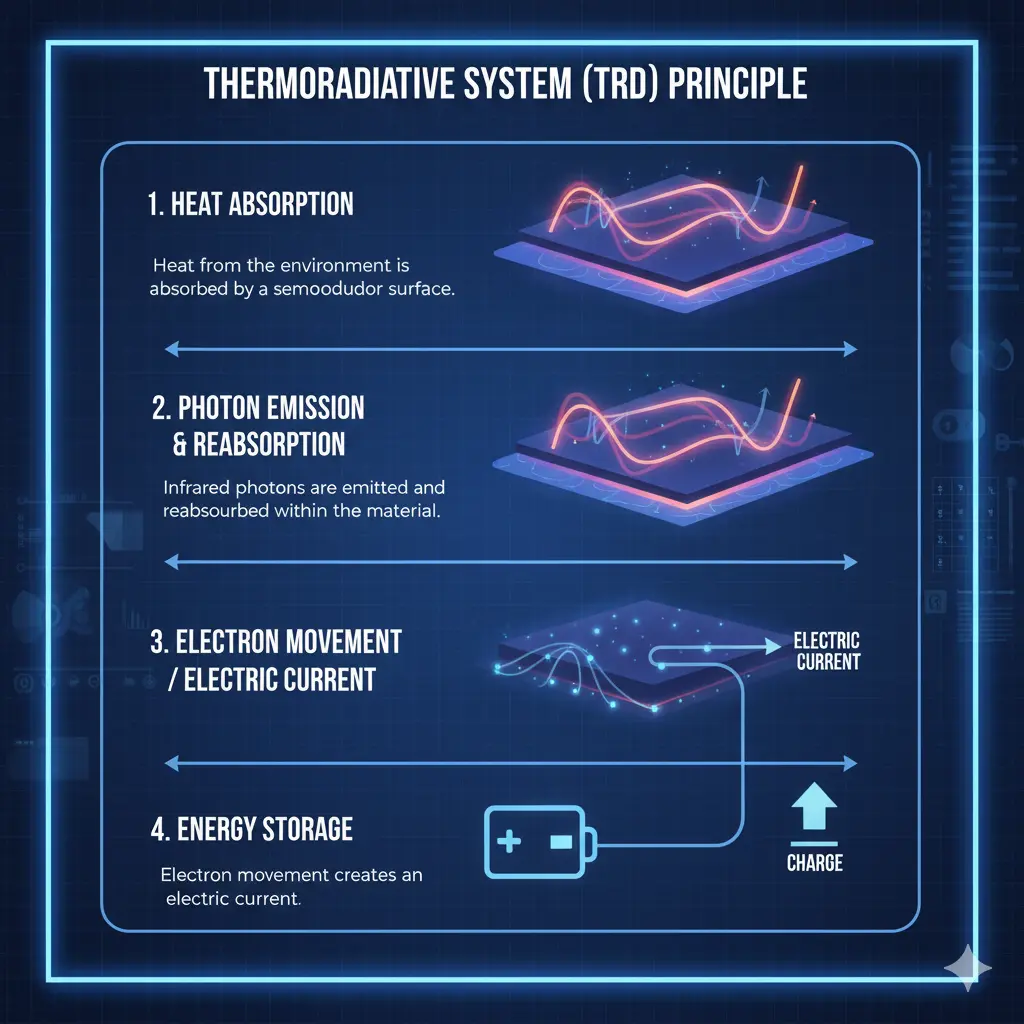
Step-by-Step: How Energy is Generated
- Heat absorption: The semiconductor layer absorbs heat from the surrounding environment or surface.
- Infrared photon emission: The TRD cell emits and reabsorbs infrared photons to create an energy exchange process.
- Electron excitation: Photon energy causes electrons within the semiconductor to move, generating an electric current.
- Energy utilization: The generated electricity can be used instantly or stored for later consumption.
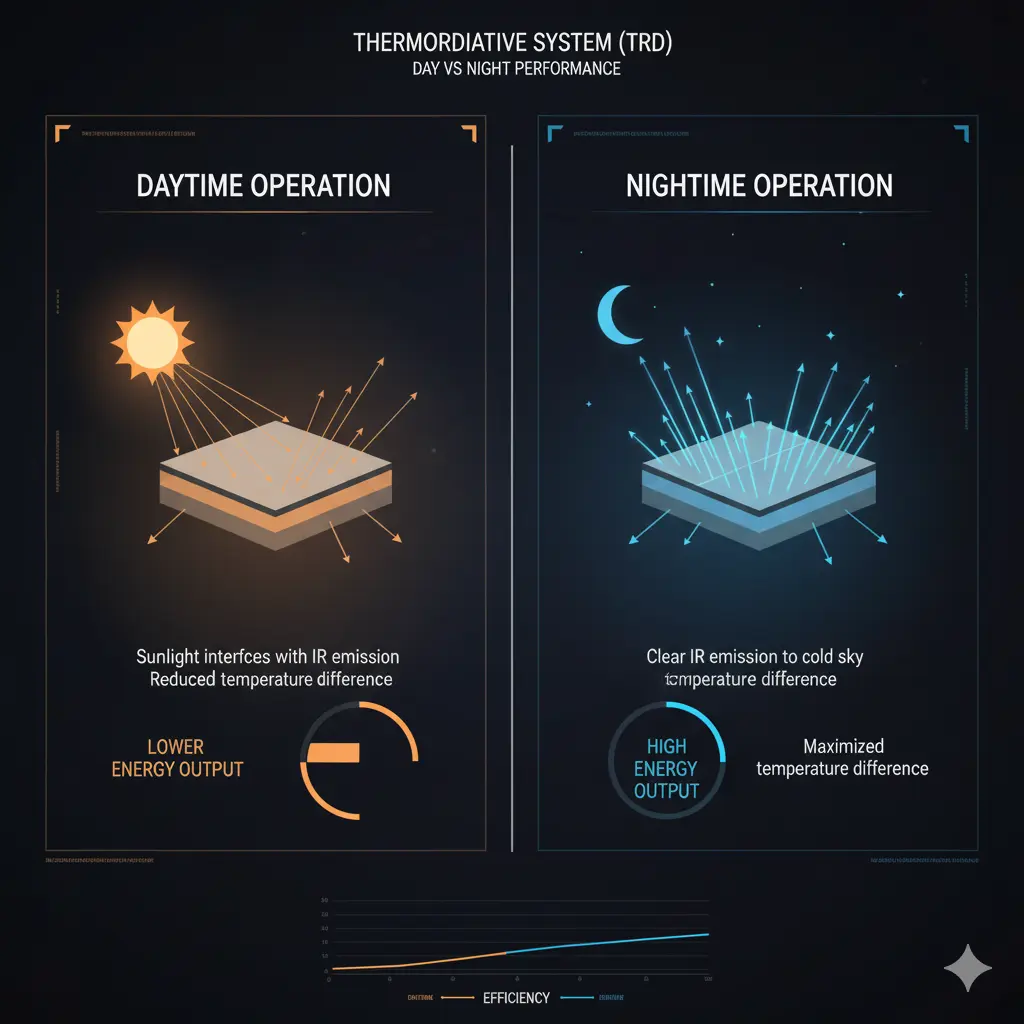
Day vs. Night Efficiency
- During the day, TRD efficiency remains moderate due to competition with incoming solar radiation.
- At night, when infrared radiation is at its peak, TRD cells perform most efficiently, utilizing thermal radiative cooling to enhance power output.
- The combination of high-quality semiconductors and temperature gradients significantly boosts overall system performance.
Advanced Technical Insights
• Quantum efficiency allows TRD systems to capture and convert low-energy photons into electricity.
• Near-infrared and mid-infrared radiation play a crucial role in night-time energy generation.
• Power conversion is possible even at ambient temperatures, although higher thermal gradients can further improve efficiency.
• TRD devices operate as reverse solar cells, emitting radiation to generate current in the opposite direction of standard photovoltaics.
Importance and Benefits of Thermoradiative System
Thermoradiative System (TRD) is emerging as a revolutionary solution in the global energy landscape. With its ability to generate power 24/7 — even during the night — TRD addresses one of the biggest limitations of traditional solar systems. This makes it an ideal technology for regions facing inconsistent sunlight or frequent power shortages.
Unlike conventional energy systems, TRD relies on thermal radiation and infrared emission, enabling it to produce clean electricity without depending solely on sunlight. As a result, it offers a sustainable and low-carbon alternative that supports global efforts toward renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Furthermore, Thermoradiative Systems can play a vital role in remote locations, off-grid areas, and industrial setups by converting waste heat into usable electricity. Once commercialized, TRD technology has the potential to significantly reduce long-term energy costs, making it a practical choice for homes, businesses, and even space applications.
⚡ Key Global Benefits
• Continuous 24/7 electricity generation — including at night
• Eco-friendly and sustainable with minimal carbon footprint
• Compatible with solar PV and wind systems for hybrid setups
• Ideal for both urban and off-grid applications
• Can utilize industrial waste heat for extra power generation
• Supports global decarbonization and clean energy goals
• Reduces dependency on fossil fuels and grid-based systems
🚀 NASA Research on Thermoradiative Cells
NASA has conducted extensive research on Thermoradiative Systems (TRD), focusing on their potential for space missions and night-time energy generation.
The core objective of NASA’s studies is to understand how infrared radiation and advanced semiconductor materials can convert low-grade heat into usable electricity with high efficiency — even in environments with no sunlight.
👉 For detailed insights and official research data, you can visit NASA’s Radioisotope Thermoradiative Cell Power Generator project page, which highlights ongoing advancements in thermoradiative energy technology.
🔬 Key Highlights from NASA Research
- Successful testing of lab-scale thermoradiative cell prototypes
- Development of advanced semiconductors designed for maximum photon absorption
- Exploration of infrared-based electricity generation in low-light or dark environments
🌌 Applications Under Study
- Satellites and space stations
- Lunar bases and extraterrestrial habitats
- Integration with hybrid renewable systems for 24/7 power generation
Quick Insights:
- Lab-scale prototypes have shown promising results.
- High-efficiency infrared semiconductors are being optimized.
- Potential for both space and terrestrial energy applications.
Future Prospects and Government Initiatives
Globally, the future of Thermoradiative Systems looks promising as governments and private sectors are investing in clean energy innovation.
In Pakistan and other developing regions, TRD can play a major role in stabilizing off-grid power supply and reducing dependence on costly fossil fuels.
Government-backed research institutions and public-private collaborations are also exploring commercial-scale deployment opportunities.
Potential Future Applications
- Integration with smart grids and urban energy planning
- Off-grid microgrid solutions for rural communities
- Industrial waste heat recovery and hybrid TRD-solar systems
Future Opportunities
- TRD integration with solar and wind power networks
- Smart energy management using IoT and AI systems
- Policy incentives and funding programs for renewable R&D
⚗️ Current Research and Development
Recent R&D efforts are pushing Thermoradiative Systems toward commercial feasibility.
NASA, along with universities and energy research labs, is testing TRD performance in both lab-controlled and environmental conditions.
Additionally, integration of TRD with energy storage systems and hybrid solar grids is under active experimentation.
| Feature | Lab-Scale TRD | Large-Scale Potential |
| Energy Output | Micro to milli-watt range | Theoretical high output |
| Deployment | Research laboratories | Urban and industrial scalability |
| Efficiency | High in controlled environments | Dependent on material innovation |
| Cost | Low for R&D | Moderate to high for production |
⚠️ Challenges and Limitations
Despite its vast potential, TRD technology still faces several challenges before global commercialization:
- Material innovation is needed to improve photon absorption and thermal efficiency.
- High production costs make large-scale deployment complex.
- Integration difficulties with existing grid infrastructure persist.
🔧 Research Opportunities Ahead
- Development of hybrid TRD + solar systems for continuous energy
- AI-controlled thermal management to enhance efficiency
- Discovery of new infrared-sensitive semiconductor materials
How to Choose the Right TRD Setup for Your Energy Needs
For individuals or organizations planning to adopt TRD technology, here are key considerations to ensure performance and long-term value:
- Energy Needs: Identify whether you need power for homes, offices, or industrial applications.
- Efficiency Rating: Choose systems with verified semiconductor quality and night-time performance.
- Cost & ROI: Evaluate installation expenses versus long-term electricity savings.
- Maintenance: Prefer durable systems with low maintenance requirements.
| Feature | Thermoradiative System | Solar Panels |
| Night-Time Energy | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Environmental Impact | ♻️ Low | ⚙️ Moderate |
| Cost | 💰 Moderate | 💵 Low to Medium |
| Maintenance | 🔧 Low | 🧽 Medium |
| Efficiency (Infrared) | 🌙 High | ☀️ Moderate |
Conclusion – Power That Never Sleeps
The Thermoradiative System is redefining renewable energy by generating electricity even in darkness. Using infrared radiation and advanced semiconductors, it ensures continuous, eco-friendly power when solar panels rest.
With NASA-led research and global innovation, this technology holds the potential to make 24/7 clean energy a reality — reducing costs, boosting efficiency, and shaping a sustainable, energy-independent future.
FAQs
What is a Thermoradiative System?
A Thermoradiative System is an advanced energy technology that converts low-grade heat into electricity using semiconductors. It can generate power even at night through infrared radiation.
How does a Thermoradiative System work?
It absorbs infrared radiation and utilizes thermal radiative cooling principles to efficiently produce electricity — even when sunlight isn’t available.
Can Thermoradiative Systems generate electricity at night?
Yes. Unlike traditional solar panels, Thermoradiative Systems are specifically designed for night-time energy generation.
Are Thermoradiative Systems cost-effective in Pakistan?
They have strong cost-saving potential, especially once commercial-scale deployment begins and installation costs stabilize.
What are the main components of a Thermoradiative System?
Core components include semiconductors, heat collectors, radiative cooling surfaces, and electrical conversion units that transform thermal energy into usable power.
How is a Thermoradiative System different from solar panels?
Traditional solar panels depend on sunlight, whereas the Thermoradiative System generates energy at night using infrared radiation and heat emission.
What maintenance is required for Thermoradiative Systems?
These systems require minimal maintenance — primarily surface cleaning and occasional efficiency testing.
Can Thermoradiative Systems be used in urban homes?
Yes. TRD systems can be easily integrated into smart grids and rooftop energy setups, making them suitable for modern urban environments.
Is government support available for TRD in Pakistan?
Currently, Thermoradiative Systems are in the research and development phase, but future policy incentives and renewable programs may support local adoption.
What is the future potential of Thermoradiative Systems globally?
The future looks bright — from space missions and hybrid renewable systems to industrial waste heat recovery, TRD technology has immense global potential.
Readmore: How to Wire Jinko Solar Panels in Pakistan – Ultimate Guide